Deploying a webserver
In this post, I will deploy a simple NGINX webserver in my TKGI cluster.
In the same Ops Manager VM that I am using as a jumpbox, run this command to create a namespace to contain the NGINX webserver pods:
kubectl create namespace nginxRun this command to quickly create a deployment of the NGINX webserver with three replicas in the namespace that was just created.
kubectl -n nginx create deployment nginx --image nginx --replicas 3Monitor the creation of the NGINX pods until the pod status shows Running. Run this command to see status:
kubectl -n nginx get podse.g.,
$ kubectl -n nginx get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-bf5d5cf98-d6l2c 1/1 Running 0 10m
nginx-bf5d5cf98-jsfrp 1/1 Running 0 10m
nginx-bf5d5cf98-v6rlp 1/1 Running 0 10m
Then, to expose the webserver to the outside world (relative to the cluster), run the expose command to do so:
kubectl -n nginx expose deployment nginx --type LoadBalancer --port 80Get the external IP address of the Load Balancer service that was created, by running:
kubectl -n nginx get servicee.g.,
$ kubectl -n nginx get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nginx LoadBalancer 10.100.200.254 192.168.16.112 80:31639/TCP 5m23s
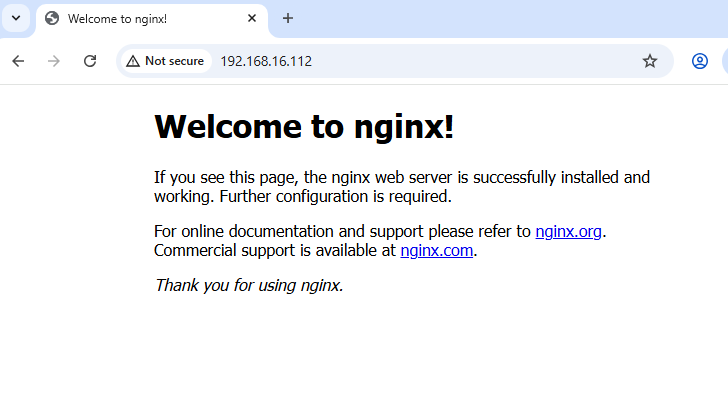
The above example shows that the Load Balancer external IP is 192.168.16.112.
The webserver should now be accessible outside the cluster, with the assumption that routing to the Floating IP CIDR is working within the environment.
From a browser, go to http://192.168.16.112 to view the NGINX webserver home page: